Navigating Your Wellness Journey with Expert Care
“Embark on with Health”
The Best Rhinoplasty Surgeon in Tijuana You Can Trust
Looking for the best rhinoplasty surgeon in Tijuana? Discover top-rated surgeons who combine expertise, advanced techniques, and affordable pricing to…
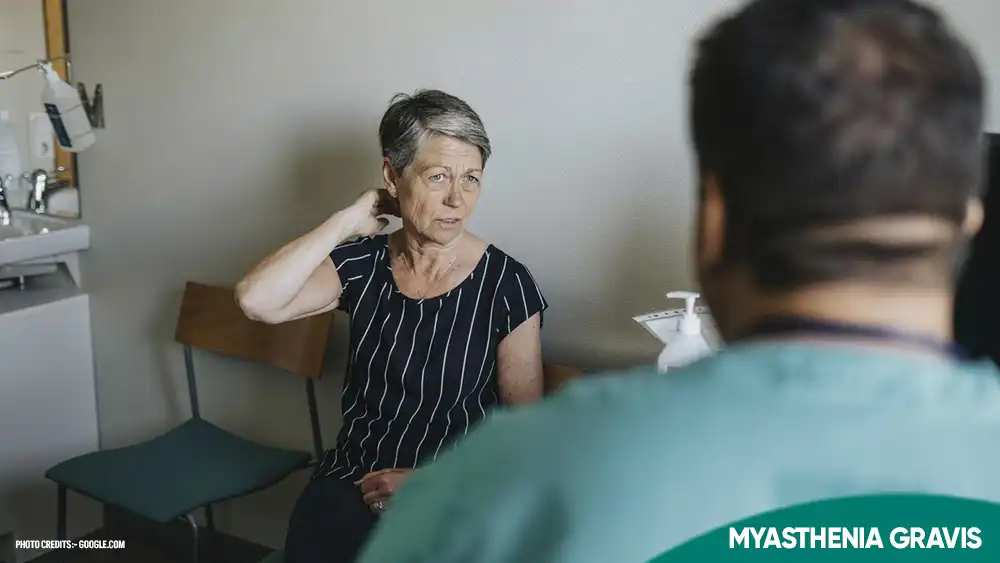
Myasthenia Gravis ICD 10: Accurate Diagnosis and Effective Management
NEUROSCIENCE Myasthenia Gravis ICD 10: Accurate Diagnosis and Effective Management Learn about the Myasthenia Gravis ICD 10 code G70.0 and…
Fairlife Protein Drink: The Ultimate Choice for Nutrition and Taste
HEALTH BLOG Fairlife Protein Drink: The Ultimate Choice for Nutrition and Taste Discover the benefits of Fairlife Protein Drink in…
Unlocking the Secret to Luscious Locks: Which Supplements Help Hair Growth
HEALTH BLOG Unlocking the Secret to Luscious Locks: What Supplements Help Hair Growth? T he health and appearance of our…
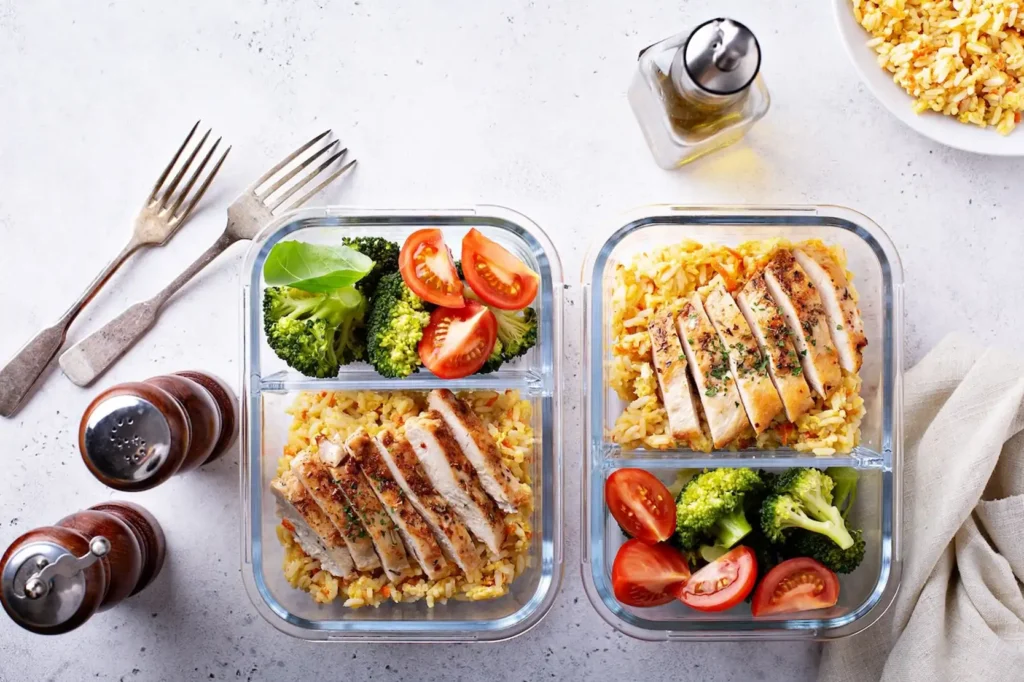
Healthy Meal Prep Ideas for Weight Loss: A Practical Guide
Discover healthy meal prep ideas for weight loss that are practical, delicious, and effective. This guide provides actionable tips for planning,…
Auther's Pick
What does syphilis look like on a man and a Woman? The best way to find out quickly
HEALTH BLOG What does syphilis look like on a man…
Mesothelioma Treatment: Navigating the Path to Recovery
HEALTH BLOG Mesothelioma Treatment: Navigating the Path to…
Does Diet Dr Pepper Have Caffeine? The Real Truth in 2024 Behind Myth
HEALTH BLOG Does Diet Dr Pepper Have Caffeine?…
Follow US
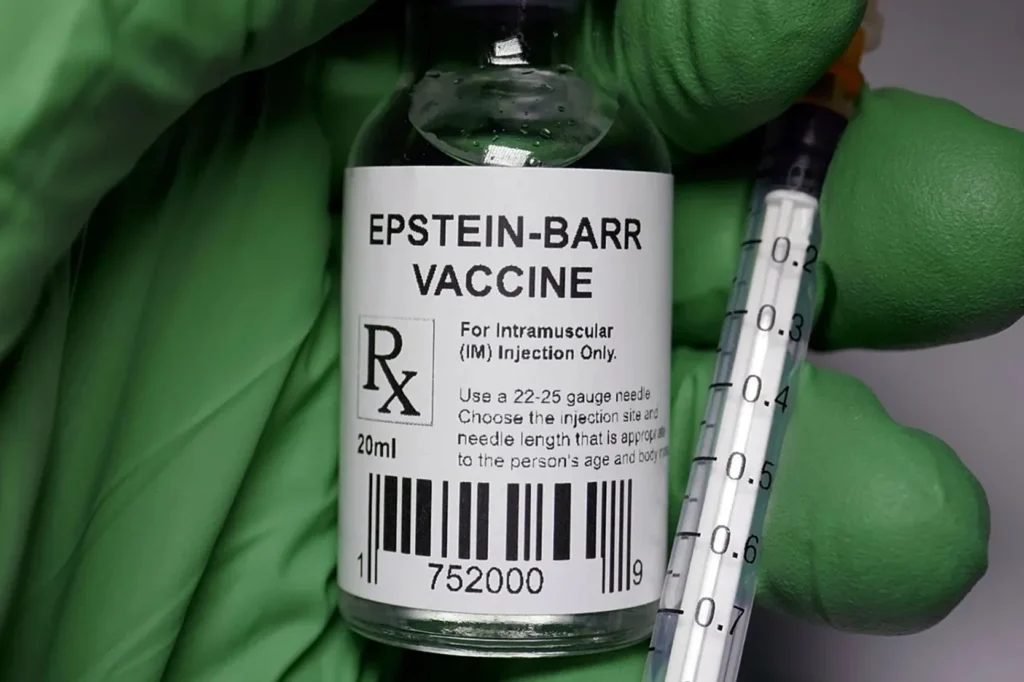
Stanford Researchers Solve Epstein Barr Virus
Discover a comprehensive guide to Epstein Barr virus (EBV), explaining what it…
Most Read
Discover Categories
Latest Updates
Really Dave Coulier Diagnosed With Tongue Cancer
He is undergoing 35 targeted radiation sessions, with a strong prognosis over 90%…
Ruth Codd Recovering After Second Leg Amputation
With prosthetics on the horizon and a sense of optimism, Ruth’s decision highlights…
Coca Cola Cherry Bring Back With Iconic Soda Flavour
This revival reflects Coke’s strategy to leverage nostalgia while innovating its product line,…
A Man Sudden Death Due to Alpha Gal Syndrome
Drawing on recent UVA research including the first documented death this post explains…
Stanford Researchers Solve Epstein Barr Virus
Learn detection methods, symptoms, prevention tips and future outlook in plain, conversational language…
Hormone Replacement Therapy is Beneficial for Women
Written with expert insight and medical accuracy, this SEO-optimized post empowers women to…
Infant Botulism Formula Recall Everone Needs to Know
Understand the science behind infant botulism, why the recall was issued, and how…
Why Cholesterol medication atorvastatin recall 2025
As an experienced healthcare professional, I help you navigate the recall with practical…
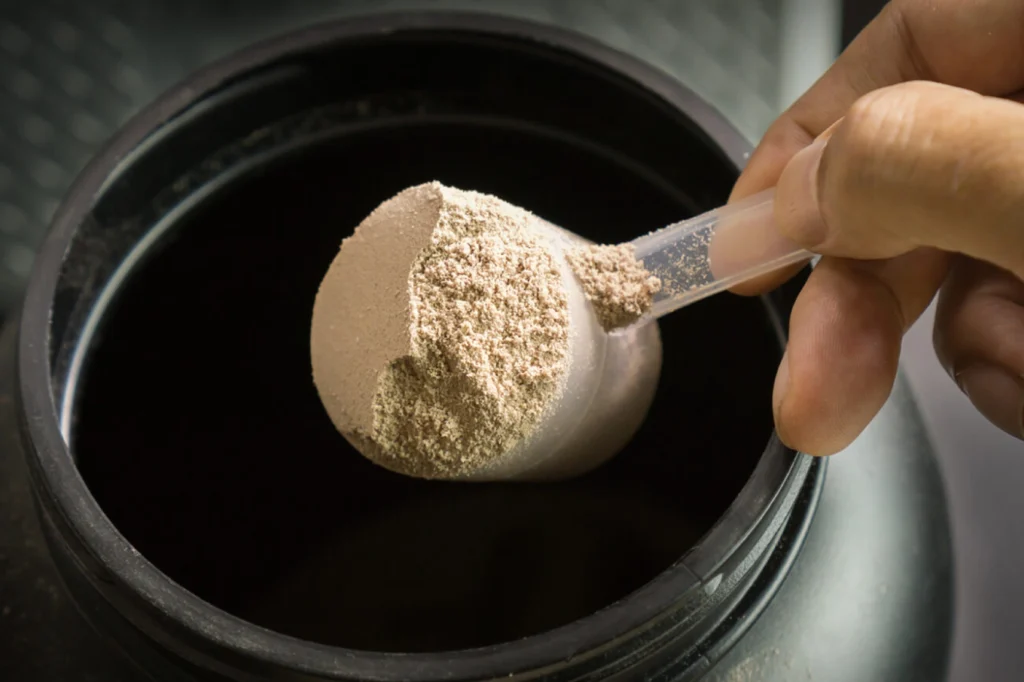
Shake and Protein Powders Contain High Levels of Lead
Learn why these metals appear in protein powders, how to identify safe brands,…
How Old Should You Be to Drink Powerade?
Learn about the drink's sugar content, absence of caffeine, and how it compares…

Find Pregnancy Related Tips Blogs!
Infant Botulism Formula Recall Everone Needs to Know
In this detailed guide, a paediatric-healthcare professional explains the recent infant botulism…
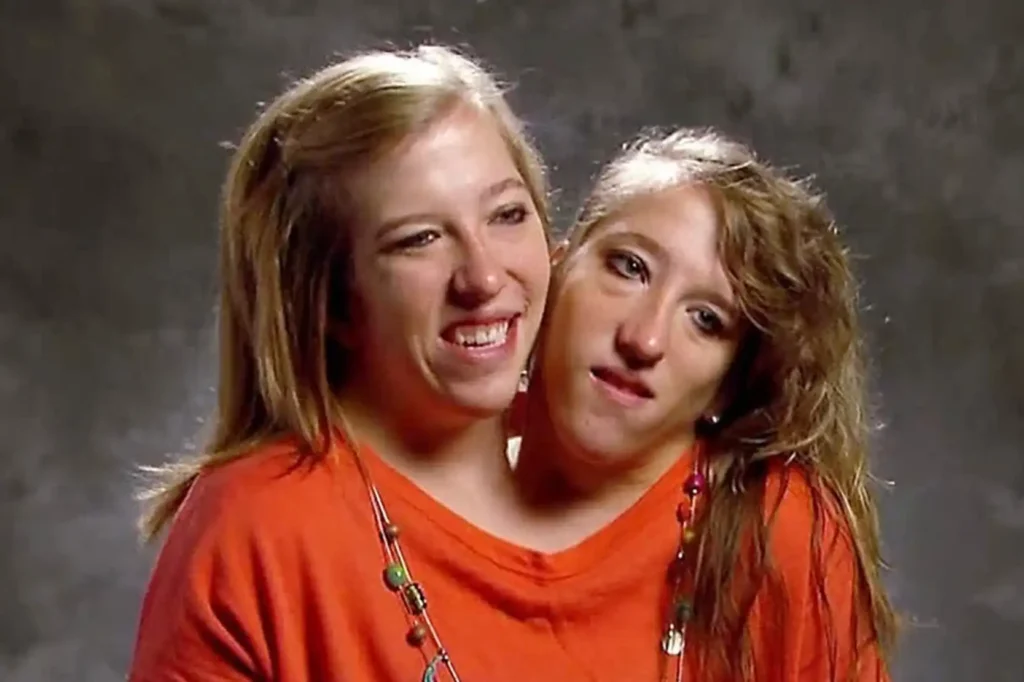
Famous Conjoined Twins Abby and Brittany Hensel Age
Abby and Brittany Hensel are 35 years old in 2025, born on…
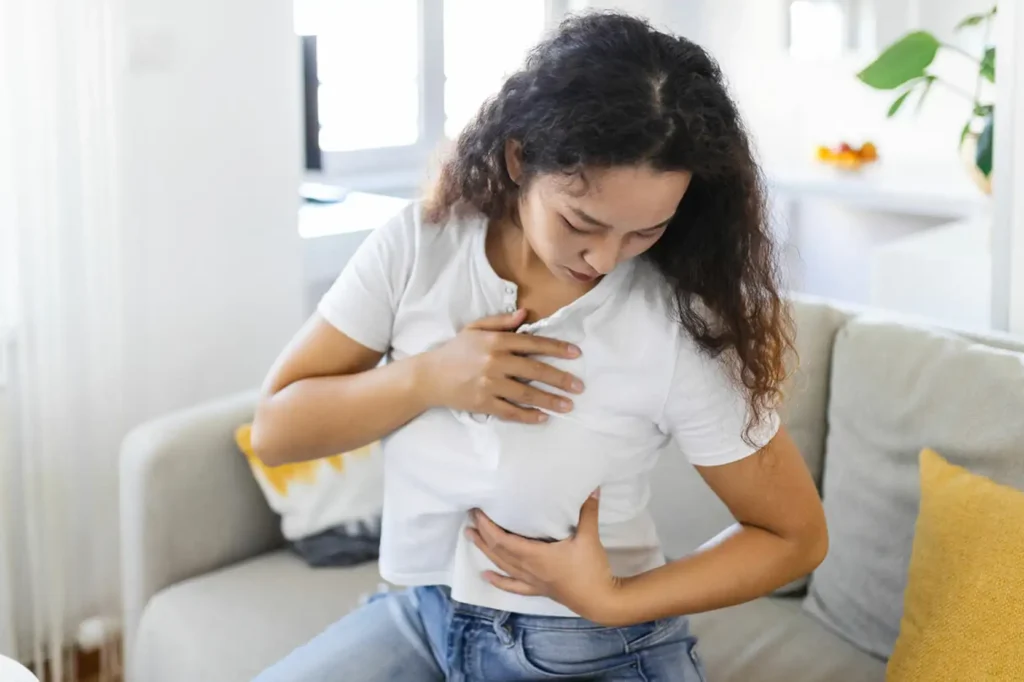
How to Identify Fibrocystic Breast Disease After Menopause
This detailed guide explains how to identify benign Fibrocystic Breast Disease After Menopause, when to seek medical help, and how lifestyle and hormone adjustments can improve breast health. With expert…
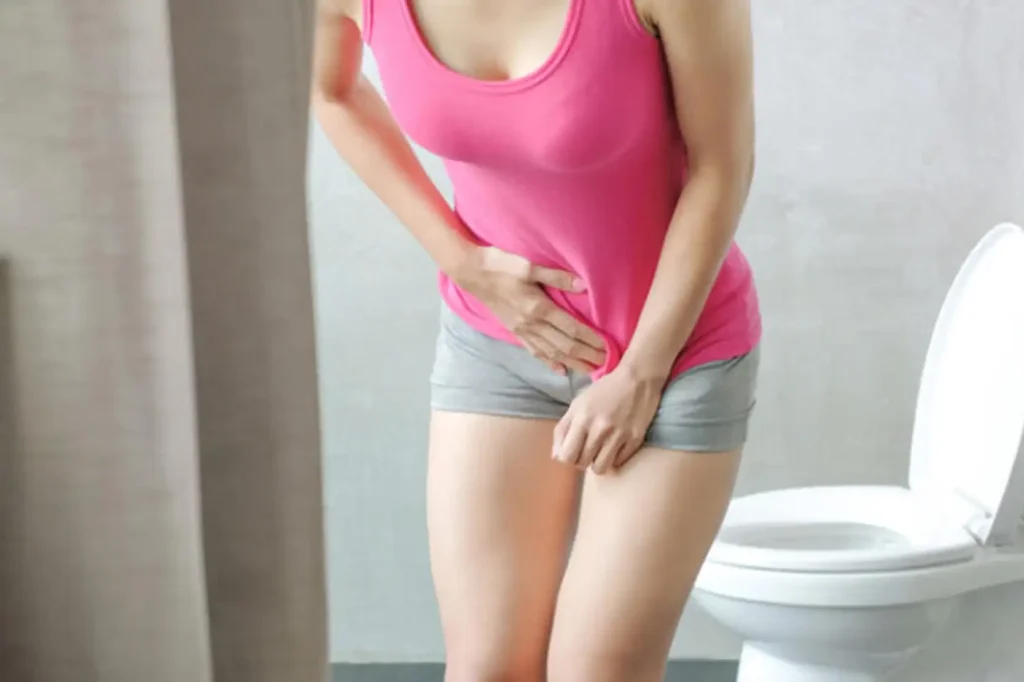
Is UTI a Sexually Transmitted Disease?
Wondering if a UTI is a sexually transmitted disease? The short answer:…
Really Dave Coulier Diagnosed With Tongue Cancer
Dave Coulier, famous for Full House, has revealed a new diagnosis: early-stage…
Ruth Codd Recovering After Second Leg Amputation
Ruth Codd, the Irish actress and social-media star, recently revealed she has…
Coca Cola Cherry Bring Back With Iconic Soda Flavour
This revival reflects Coke’s strategy to leverage nostalgia while innovating its product line, betting on long-term customer loyalty. Learn why this flavor comeback matters, how it's different this time, and…
A Man Sudden Death Due to Alpha Gal Syndrome
Alpha gal syndrome (AGS) is a growing tick-bite–induced allergy to mammalian meat…
Does Insurance Cover Therapy?
Understand in-network vs out-of-network coverage, common insurance terms, and resources for free…
Best Yoga Poses for Stress Relief: Find Your Inner Calm
With step-by-step instructions and breathing techniques, this guide helps you unwind and…
6 Natural Remedies for Anxiety: A Holistic Solutions
Discover the most effective natural remedies for anxiety to help you feel calmer and more in control. This comprehensive guide covers herbal solutions like chamomile and lavender, mindfulness practices, exercise tips,…
How Much Is the Average Asbestos Lawsuit Settlement Amount?
These settlements are a vital source of financial support for individuals suffering…