Written by an experienced health professional, this resource offers insight into early detection, recurrence risks, and what to expect during recovery. Whether you’re newly diagnosed or supporting someone, this blog provides expert guidance rooted in real medical knowledge and empathy. Understand the facts and find hope in proven treatments.
What is Gestational Trophoblastic Disease:
Gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) refers to a group of rare tumors that involve abnormal growth of cells inside a woman’s uterus after conception. These tumors originate from the trophoblastic cells, which normally develop into the placenta during pregnancy. Instead of progressing into a healthy placenta, these cells form abnormal masses or tumors, some of which can be benign (like hydatidiform moles), while others are malignant (like choriocarcinoma).
As someone with experience in reproductive health and clinical research, I can tell you that while the term sounds frightening, GTD is one of the most treatable forms of cancer-related conditions in gynecology. Early diagnosis, regular monitoring, and specialized care significantly improve outcomes, even in more severe cases.
Yes, most women can have normal pregnancies after treatment, especially if their fertility was preserved.
How Rare is Gestational Trophoblastic Disease:
GTD is a rare condition, occurring in about 1 in every 1,000 pregnancies in the U.S., and in 1 in 500 pregnancies in some Asian countries. The global incidence varies based on genetics, geographic location, and access to reproductive care. In places like Southeast Asia and parts of Africa, GTD appears slightly more frequently, likely due to nutritional factors and reproductive trends.
In developed countries with advanced prenatal care, early detection of GTD means that it’s often caught before it becomes life-threatening. However, the rarity of the condition can sometimes lead to delayed diagnosis simply because it’s not on most doctors’ radars especially if the patient isn’t seeing a specialist in reproductive medicine or gynecology.
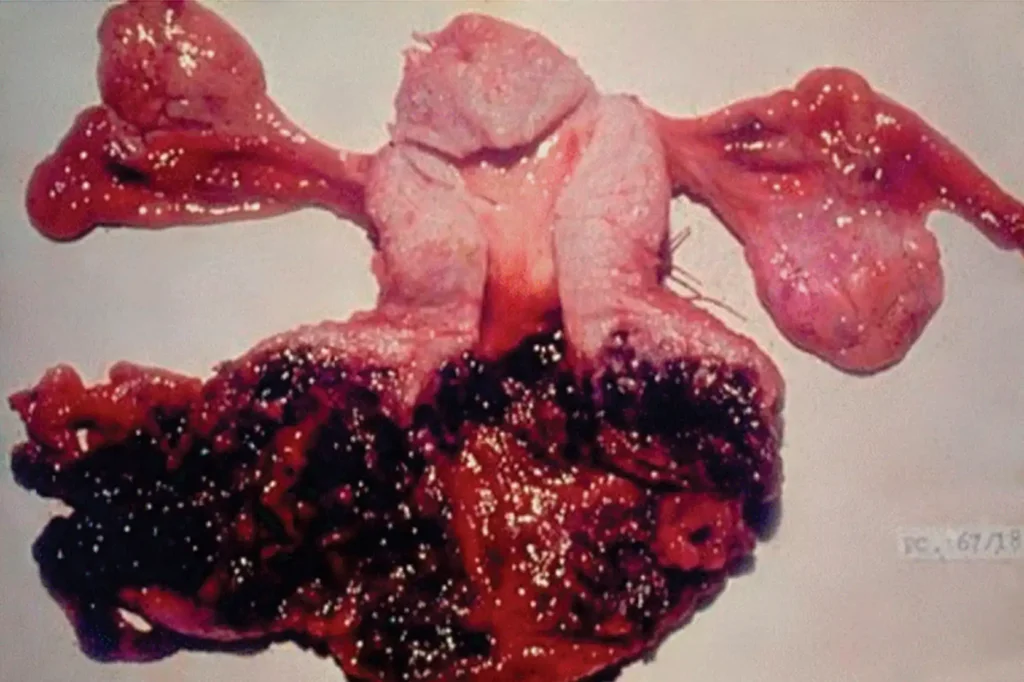
Types of Gestational Trophoblastic Disease:
There are several forms of GTD, each with different risks and clinical behaviors. Each type presents differently and requires a unique approach to management. Understanding which type of GTD you’re dealing with is crucial for tailoring the best treatment strategy.
- Hydatidiform Mole (Molar Pregnancy): This is the most common type and can be complete or partial. It involves abnormal fertilization that leads to nonviable pregnancy tissue forming in the uterus.
- Invasive Mole: A type of molar pregnancy that invades the uterine muscle. While still usually benign, it requires treatment.
- Choriocarcinoma: A malignant and fast-growing cancer that can spread to other organs. Fortunately, it responds well to chemotherapy.
- Placental Site Trophoblastic Tumor (PSTT) and Epithelioid Trophoblastic Tumor (ETT): These are very rare subtypes that can occur months or years after a pregnancy and may need surgical intervention.
What are the Risk Factors for GTD:
While anyone can develop gestational trophoblastic disease, certain factors increase the risk. If you fall into a higher-risk group, your healthcare provider may recommend closer monitoring during early pregnancy, including early ultrasound and hCG testing.
- Age: Women under 20 or over 35 have a higher risk, especially for molar pregnancies.
- Previous Molar Pregnancy: If you’ve had GTD before, your risk for recurrence is significantly higher.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: A lack of carotene (a form of vitamin A) and folic acid may play a role in some populations.
- Geographic Location: As mentioned earlier, GTD rates are higher in some countries due to a mix of genetics and environmental factors.
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For:
Most women discover they have GTD during early pregnancy scans or after experiencing unusual symptoms. Common signs include. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s critical to get an evaluation right away. Early detection improves outcomes dramatically, especially for malignant forms of GTD.
- Heavy vaginal bleeding during pregnancy
- A uterus that’s larger than expected for gestational age
- Severe nausea and vomiting (hyperemesis gravidarum)
- High hCG levels with no fetal heartbeat
- Passage of grape-like cysts from the vagina (classic for molar pregnancy)
Diagnosis and How It’s Confirmed:
Doctors typically begin with a pelvic ultrasound and blood tests measuring human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). GTD often causes extremely high hCG levels that don’t align with typical pregnancy progress. In some cases, doctors may perform a dilation and curettage (D&C) to remove the abnormal tissue and confirm the diagnosis through lab analysis.
Biopsy and histopathological tests are also used to classify the type of GTD. Imaging scans like CT or MRI may be recommended if doctors suspect spread beyond the uterus, especially in cases like choriocarcinoma.
Treatment Options and Prognosis:
Most forms of GTD, even cancerous ones like choriocarcinoma, are highly treatable, especially when caught early. Treatment plans typically include.
- Dilation and Curettage (D&C): Used to remove abnormal tissue from the uterus.
- Chemotherapy: Used for malignant forms, often with excellent response rates.
- Hysterectomy: In rare cases or for women who do not wish to maintain fertility.
Can GTD Come Back:
Recurrence is rare but possible, particularly in women who’ve had a previous molar pregnancy or incomplete follow-up. That’s why long-term monitoring is essential. Most guidelines recommend checking hCG levels weekly until they normalize, then monthly for up to 6–12 months. If GTD does return, it’s still treatable, and most patients go on to have healthy pregnancies afterward if fertility is preserved.
FAQ
Most frequent questions and answers
Yes, most women can have normal pregnancies after treatment, especially if their fertility was preserved.
Not always. Some types, like molar pregnancies, are benign. Others, like choriocarcinoma, are cancerous but highly treatable.
Unusual bleeding, very high hCG levels, and absence of fetal heartbeat are common signs. An early ultrasound is essential.
Conclusion:
While its rarity can delay diagnosis, the good news is that GTD is highly treatable with early detection and proper care, how rare is gestational trophoblastic disease depends on various factors, but it remains an uncommon condition, affecting roughly 1 in 1,000 pregnancies in developed countries. Understanding the signs, risk factors, and treatment options empowers women to take charge of their reproductive health. If diagnosed, know that recovery and even future healthy pregnancies are absolutely possible.