HEALTH NEWS
HIV Medication Cost: Impact, Barriers, and Paths to Affordability
-
Rahul Priydarss
Discover the critical role of HIV medication cost in managing HIV/AIDS and the complexities surrounding its cost. Explore factors influencing medication expenses, from brand vs. generic options to insurance coverage and government subsidies. Learn about strategies to alleviate the financial burden, ensuring access to life-saving treatment for individuals living with HIV/AIDS. Dive into the implications of medication costs on patients, healthcare systems, and society, and explore actionable steps toward affordability.
Introduction to HIV Medication Cost:
HIV medication plays a crucial role in managing the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS). Understanding the significance of HIV medication and the factors influencing its cost is essential for individuals living with HIV/AIDS, healthcare providers, and policymakers.
What is Hiv (Human Immunodeficiency Virus):
HIV, which stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus, is a virus that attacks the body’s immune system, specifically targeting CD4 cells, also known as T cells, which help the immune system fight off infections. Over time, HIV can destroy so many of these cells that the body becomes unable to fight off infections and diseases effectively. This weakening of the immune system can lead to a condition called AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome), which is the final stage of HIV infection.

Table of Contents
Understanding the Significance of HIV Medication:
HIV medication, often referred to as antiretroviral therapy (ART), is a lifeline for individuals diagnosed with HIV/AIDS. These medications work by suppressing the replication of the virus in the body, reducing the viral load, and preventing the progression of HIV to AIDS. With consistent adherence to medication regimens, people living with HIV can lead longer, healthier lives and significantly reduce the risk of transmitting the virus to others.
Forty Years Ago The Emergence of HIV/AIDS:
Forty years ago, the landscape of healthcare in the United States was vastly different. Terms like HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) and AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) were not part of the common vernacular, and the specter of a mysterious illness was yet to cast its shadow over the nation. It was the early 1980s when the first cases of what would later be identified as HIV/AIDS emerged, marking the beginning of a profound and devastating chapter in medical history.
The initial reports of this enigmatic disease puzzled researchers and healthcare professionals alike. Afflicting individuals seemingly at random, its symptoms were varied and often severe, ranging from opportunistic infections to rare cancers. In those early years, the medical community scrambled to comprehend the nature of this new threat and to develop effective strategies for diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
Overview of Factors Influencing HIV Medication Cost:
The cost of HIV medication is influenced by various factors, ranging from the type of medication to insurance coverage and government policies. Brand-name medications often come with higher price tags compared to generic alternatives. Additionally, insurance coverage, copayments, and geographic location can significantly impact out-of-pocket expenses for individuals accessing HIV medication. Government subsidies and assistance programs play a crucial role in providing financial support to those in need, but the availability and accessibility of such programs vary across regions.
HIV Medication Cost and Some Rx Medicine:
Drug Name (Brand Name) | Cost of Brand Name
- Advertisement -
| Generic Available | Number of Tablets or Capsules | Strength |
etravirine (Intelence) | $1,477
- Advertisement -
| Yes | 60 | 200 mg |
efavirenz (Sustiva) | $94
- Advertisement -
| Yes | 90 | 200 mg |
nevirapine (Viramune) | $30
- Advertisement -
| Yes | 60 | 200 mg |
rilpivirine (Edurant) | $1,320
- Advertisement -
| No | 30 | 25 mg |
lamivudine/zidovudine (Combivir) | $810
- Advertisement -
| Yes | 60 | 150 mg/300 mg |
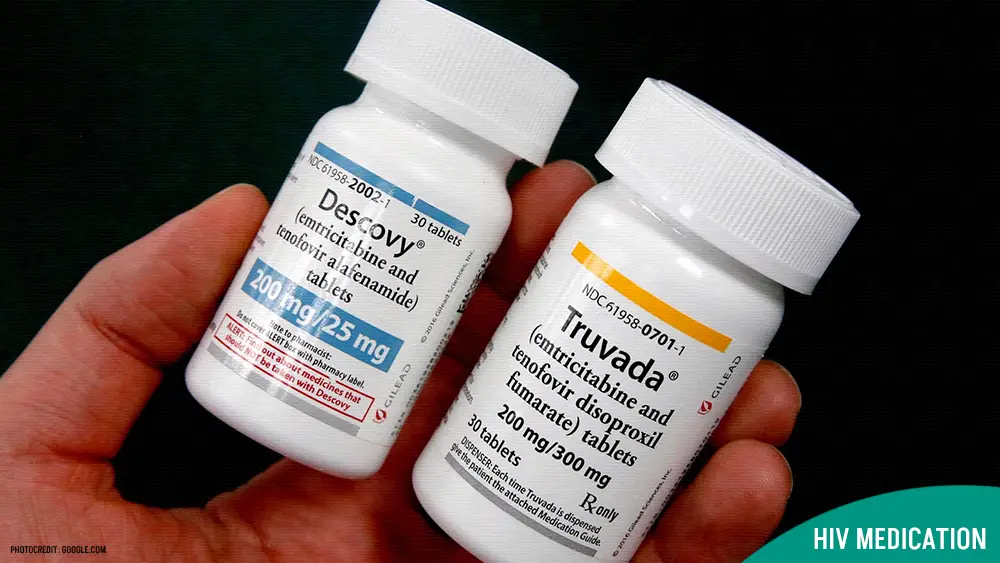
emtricitabine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (Truvada) | $266
- Advertisement -
| Yes | 30 | 200 mg/300 mg |
emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide (Descovy) | $2,530
- Advertisement -
| No | 30 | 200 mg/25 mg |
abacavir (Ziagen) | $605
- Advertisement -
| Yes | 60 | 300 mg |
emtricitabine (Emtriva) | $560
- Advertisement -
| Yes | 30 | 200 mg |
tenofovir alafenamide fumarate (Vemlidy) | $1,269
- Advertisement -
| No | 30 | 25 mg |
Types of HIV Medications:
These different types of HIV medications play crucial roles in HIV prevention, treatment, and management, contributing to efforts to control the spread of the virus and improve the health outcomes of individuals living with HIV/AIDS.
Antiretroviral Therapy (ART):
- ART involves a combination of medications used to treat HIV infection.
- These medications work by inhibiting the replication of the virus in the body.
- ART aims to suppress the HIV Virus, allowing the immune system to recover and function effectively.
- It typically involves taking a combination of different drugs, such as nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs), non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs), protease inhibitors (PIs), and integrase inhibitors (INSTIs).
- ART has revolutionized HIV treatment, significantly prolonging the lifespan of individuals living with HIV/AIDS and reducing the risk of transmission to others.
Pre-exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP):
- PrEP is a preventive medication regimen taken by individuals at high risk of HIV infection.
- It involves taking a single pill daily containing a combination of antiretroviral drugs, typically tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and emtricitabine.
- PrEP works by blocking the replication of the virus in the event of exposure, reducing the risk of HIV acquisition.
- It is highly effective when taken consistently and as prescribed, offering protection against HIV transmission from infected partners.
- PrEP is recommended for individuals who engage in high-risk behaviors, such as unprotected sex or sharing needles, and for serodiscordant couples where one partner is HIV-positive and the other is not.
Post-exposure Prophylaxis (PEP):
- PEP is a short-term medication regimen initiated after potential exposure to HIV to prevent infection.
- It involves taking a combination of antiretroviral drugs for a specified duration, ideally within 72 hours of exposure.
- PEP works by inhibiting viral replication and preventing the establishment of HIV infection in the body.
- It is typically recommended for individuals who have experienced high-risk exposure to HIV, such as needlestick injuries or unprotected sex with an HIV-positive partner.
- PEP should be initiated as soon as possible after exposure and continued for a 28-day course to maximize effectiveness in preventing HIV infection.
Effecting Factors for HIV Medication Cost:
These factors collectively contribute to the overall cost of HIV medication, influencing accessibility and affordability for individuals living with HIV/AIDS.
Brand vs. Generic Medications:
- Brand-name HIV medications often come with higher price tags compared to their generic counterparts.
- Generic versions of HIV drugs are typically more affordable as they are produced after the patent on the brand-name drug expires.
- The choice between brand and generic medications can significantly impact the overall cost of HIV treatment.
Insurance Coverage and Copays:
- The extent of insurance coverage for HIV medication varies depending on the individual’s insurance plan.
- Insurance plans may have different levels of coverage for prescription medications, including copays, deductibles, and coverage limits.
- Individuals with comprehensive insurance coverage may have lower out-of-pocket expenses for HIV medication compared to those with limited or no coverage.
Geographic Location:
- HIV medication costs can vary based on geographic location and healthcare infrastructure.
- Access to affordable medication may be more challenging in rural or underserved areas where healthcare resources are limited.
- Urban areas with greater access to healthcare facilities and pharmacies may offer more competitive pricing for HIV medications due to increased market competition.
Government Subsidies and Assistance Programs:
- Government-funded programs and subsidies play a crucial role in reducing the cost of HIV medication for eligible individuals.
- Programs like the Ryan White HIV/AIDS Program in the United States provide financial assistance for HIV medication and related healthcare services to low-income individuals.
- These assistance programs help bridge the affordability gap and ensure access to life-saving HIV treatment for those in need.
Burden of HIV Medication Cost on Patients:
The burden of HIV medication cost on patients is substantial and multifaceted, encompassing various challenges and implications.
Financial Strain:
- The high cost of HIV medication can impose significant financial strain on patients, particularly those without adequate insurance coverage or financial resources.
- Out-of-pocket expenses for HIV medication, including copays, deductibles, and other related costs, can become overwhelming, leading to financial hardship and potential economic instability.
Access to Treatment:
- Affordability issues may hinder patients’ ability to access essential HIV medications, jeopardizing their health and well-being.
- Patients may face barriers in obtaining prescribed medications due to cost concerns, leading to delays or interruptions in treatment.
Adherence Challenges:
- Financial constraints related to medication costs can impact patients’ adherence to prescribed treatment regimens.
- Patients may skip doses, ration medications, or delay refills to stretch their supply or minimize expenses, compromising the effectiveness of treatment.
Health Consequences:
- Non-adherence to HIV medication regimens due to cost concerns can have serious health consequences for patients.
- Suboptimal adherence may result in treatment failure, disease progression, development of drug resistance, and increased risk of opportunistic infections and other complications.
Psychological Stress:
- The burden of HIV medication cost can also contribute to psychological stress and anxiety among patients.
- Fear of not being able to afford medications, uncertainty about future costs, and worries about managing financial obligations alongside healthcare expenses can negatively impact patients’ mental well-being.
Social Impacts:
- Financial challenges related to HIV medication cost may affect various aspects of patients’ lives, including their relationships, employment, and social activities.
- Patients may experience social isolation, stigma, and discrimination due to their inability to afford medications or access necessary healthcare services.
Plan for Reducing HIV Medication Cost:
To reduce the burden of HIV medication costs and improve access to affordable treatment, a comprehensive plan can be implemented, focusing on various strategies.
Promote Generic Medications:
- Encourage the use of generic versions of HIV medications, which are typically more affordable than brand-name drugs.
- Increase awareness among healthcare providers and patients about the availability and efficacy of generic alternatives.
Enhance Insurance Coverage:
- Advocate for comprehensive insurance coverage that includes HIV medications with minimal copays and deductibles.
- Work with insurers to expand coverage options and reduce financial barriers for patients.
Negotiate Drug Pricing:
- Engage in negotiations with pharmaceutical companies to lower the cost of HIV medications through bulk purchasing or price agreements.
- Leverage government purchasing power and regulatory mechanisms to negotiate fair prices for essential medications.
Expand Government Subsidies:
- Allocate additional funding to government subsidy programs, such as the Ryan White HIV/AIDS Program, to provide financial assistance for HIV medication to low-income individuals.
- Expand eligibility criteria and coverage under existing subsidy programs to reach more patients in need.
Increase Access to Patient Assistance Programs:
- Raise awareness about patient assistance programs offered by pharmaceutical companies, which provide free or discounted medications to eligible individuals.
- Assist with navigating the application process and accessing available resources for patients in need.
Facilitate Generic Drug Production:
- Support initiatives to promote the production of generic HIV medications by generic drug manufacturers.
- Provide incentives and regulatory support to encourage the development and distribution of generic alternatives.
Implement Price Controls:
- Enact policies to regulate the pricing of HIV medications and prevent excessive price hikes.
- Implement price transparency measures to ensure accountability and fairness in drug pricing.
Strengthen Healthcare Infrastructure:
- Invest in healthcare infrastructure, including clinics, pharmacies, and distribution networks, to improve access to HIV medication in underserved areas.
- Expand telemedicine and telepharmacy services to reach remote and rural populations with limited access to healthcare facilities.
Support Research and Development:
- Invest in research and development initiatives focused on developing innovative and cost-effective treatments for HIV/AIDS.
- Promote collaborations between academia, industry, and government agencies to accelerate the discovery and development of new therapies.
Advocate for Policy Changes:
- Advocate for policy changes at the local, national, and international levels to address systemic barriers to affordable HIV medication.
- Mobilize stakeholders, including healthcare providers, advocacy groups, and policymakers, to support legislative and regulatory reforms aimed at reducing medication costs.
FAQs about HIV Medication Cost:
A1: HIV medications include antiretroviral therapy (ART), pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), and post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP). Each type serves a different purpose in HIV prevention and treatment.
A2: HIV medications work by suppressing the replication of the virus in the body, reducing the viral load, and preventing the progression of HIV to AIDS. ART aims to keep the virus in check, while PrEP and PEP are used for prevention in high-risk individuals.
A3: Generic medications are often more affordable than brand-name drugs, making them accessible to a larger population. They contain the same active ingredients as brand-name drugs and undergo rigorous testing to ensure safety and efficacy.
A4: The cost of HIV medication can be influenced by factors such as brand vs. generic medications, insurance coverage, geographic location, and government subsidies. These factors can vary widely and impact the affordability of treatment for individuals living with HIV/AIDS.
A5: Patients can access financial assistance through patient assistance programs offered by pharmaceutical companies and government subsidy programs like the Ryan White HIV/AIDS Program. These programs provide support to eligible individuals who cannot afford HIV medication.
-Please remember, to always consult with healthcare professionals or Doctors for personalized advice related to medical conditions.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the HIV medication cost is a critical aspect of managing HIV/AIDS, impacting individuals, healthcare systems, and society as a whole. As outlined in this article, understanding the significance of HIV medication and the factors influencing its cost is essential for effective treatment, prevention, and policy development. HIV medication, including antiretroviral therapy (ART), pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), and post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP), plays a vital role in controlling the virus, improving health outcomes, and reducing transmission rates. However, the high cost of medication can pose significant challenges for patients, leading to financial strain, access barriers, and adherence issues.




