HEALTH NEWS
Post Polio Syndrome ICD-10 Code and Treatment, Clinical Features
-
 Rahul Priydarss
Rahul Priydarss - February 24, 2024
Discover comprehensive insights into Post Polio Syndrome ICD10 with an exploration of its diagnosis using the ICD-10 code G14.0. Uncover symptoms, management strategies, and expert guidance for living with this condition. Dive into a detailed discussion created with the latest research and human-written content expertise.
What Is Post Polio Syndrome ICD-10:
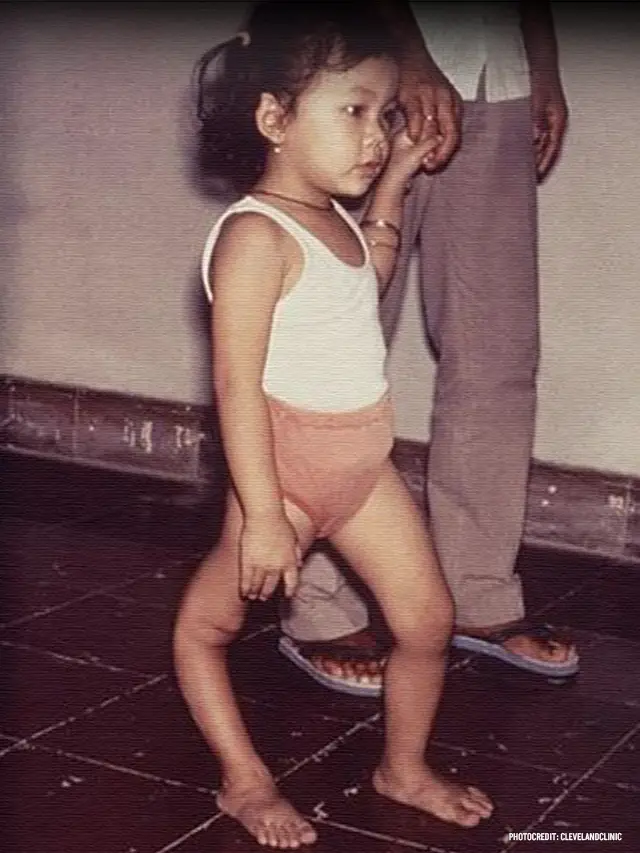
Post Polio Syndrome ICD 10 (PPS) is a complex condition that affects individuals who have previously experienced poliomyelitis, commonly known as polio. While polio itself is caused by a viral infection, PPS emerges years after the initial recovery from the acute illness. It is characterized by a range of symptoms such as muscle weakness, fatigue, and pain, which can significantly impact the quality of life of affected individuals. In medical coding systems, such as the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision (ICD-10), PPS is identified by the code G14.0.
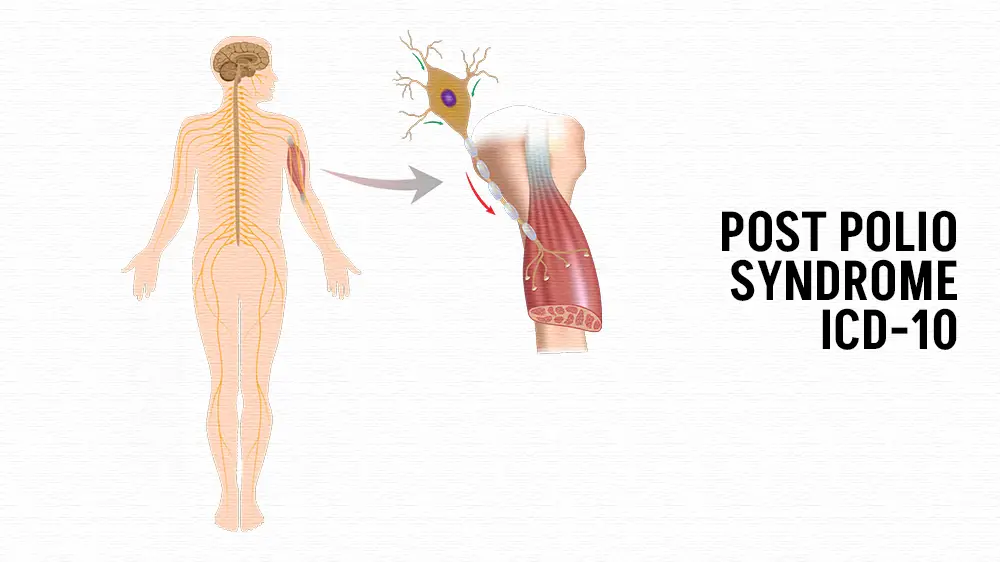
Table of Contents
Clinical Features of Post Polio Syndrome ICD-10:
Post-Polio Syndrome ICD 10 typically manifests years after the initial polio infection, often appearing 15 to 40 years later. Its clinical presentation varies among individuals, but common symptoms include:
- Muscle Weakness: PPS’s progressive weakness in muscles previously affected by polio is a hallmark feature. This weakness can impact mobility and everyday activities.
- Fatigue: Individuals with PPS often experience excessive fatigue that is not alleviated by rest. This fatigue can be debilitating and affect overall functioning.
- Muscle Atrophy: Gradual wasting away or shrinkage of muscles affected by prior polio infection may occur in PPS, contributing to weakness and functional impairment.
- Pain: Muscle and joint pain are common symptoms of PPS. This pain may be chronic and interfere with daily activities and quality of life.
- Mobility Issues: Difficulty with mobility, including walking and performing tasks requiring muscle strength, is common in individuals with PPS.
- Respiratory Problems: Some individuals with PPS may experience respiratory difficulties, such as shortness of breath or decreased lung function.
- Swallowing Difficulties: Weakness in the muscles involved in swallowing may lead to swallowing difficulties or aspiration in individuals with PPS.
- Sleep Disturbances: Insomnia, disrupted sleep patterns, or excessive daytime sleepiness may occur in people with PPS, further exacerbating fatigue and other symptoms.
- Cold Intolerance: Heightened sensitivity to cold temperatures, particularly in affected muscles, is reported by some individuals with PPS.

Management and Treatment of Post Polio Syndrome ICD-10:
While there is no cure for Post Polio Syndrome, various strategies can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. These may include.
- Physical Therapy: Targeted exercise programs and physical therapy can help improve muscle strength, mobility, and endurance.
- Assistive Devices: Mobility aids such as braces, orthotics, or wheelchairs may be recommended to improve mobility and reduce strain on weakened muscles.
- Pain Management: Medications, physical modalities, and other pain management techniques can help alleviate PPS-related muscle and joint pain.
- Energy Conservation: Learning energy conservation techniques and pacing activities can help manage fatigue and optimize energy levels.
- Respiratory Support: Respiratory therapy and interventions may be necessary for individuals with respiratory complications to improve breathing and lung function.
- Psychosocial Support: Counseling and support groups can provide emotional support and coping strategies for individuals living with PPS and their caregivers.
FAQs Post Polio Syndrome ICD-10:
A1: Post Polio syndrome is believed to occur due to the degeneration of nerve cells in the spinal cord that was previously damaged by the poliovirus.
A2: Currently, there is no cure for PPS. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
A3: Diagnosis of PPS is typically based on a patient’s medical history, symptoms, and physical examination. Additional tests, such as electromyography (EMG), may be performed to assess muscle function.
A4: Since there is no specific prevention for PPS, efforts focus on preventing initial polio infection through vaccination.
A5: The prognosis varies for each individual with PPS. While symptoms may worsen over time, many people can effectively manage their symptoms and maintain a good quality of life with proper treatment and support.
-Please remember, to always consult with healthcare professionals or Doctors for personalized advice related to medical conditions.
Conclusion:
Post Polio syndrome ICD-10 code G14.0, is a chronic condition that affects individuals who have previously experienced polio. Characterized by muscle weakness, fatigue, pain, and other symptoms, PPS can significantly impact quality of life. Healthcare professionals play a crucial role in diagnosing, managing, and supporting individuals with PPS to optimize their well-being and functional independence. Through a multidisciplinary approach incorporating medical interventions, rehabilitation, and psychosocial support, individuals with PPS can better cope with the challenges posed by the condition and lead fulfilling lives.