HEALTH BLOG
Surgical Varicocele Treatment and Diagnosis for Recovery, a Complete Overview
-
 Rahul Priydarss
Rahul Priydarss - March 6, 2024
Discover the comprehensive guide to surgical varicocele treatment and diagnosis for recovery. Learn about the causes, symptoms, and prevalence of varicoceles, along with the criteria for surgical intervention. Explore the various surgical techniques, recovery timelines, potential complications, and success rates. Gain insights from patient testimonials and FAQs to make informed decisions about addressing varicocele-related challenges effectively.
Understanding Varicocele:
Varicocele is a condition characterized by the enlargement of veins within the scrotum, specifically the veins that drain the testicles. These veins, known as the pampiniform plexus, can become dilated and twisted, leading to a varicocele. This condition is similar to varicose veins that occur in the legs.
Prevalence:
Varicoceles are relatively common, affecting approximately 15% of males. They are most commonly diagnosed in young men, typically between the ages of 15 and 25, although they can occur at any age.
Table of Contents
Causes:
The precise cause of varicoceles isn’t always clear, but several factors may contribute to their development.
Faulty valves in the veins: The veins in the scrotum have valves that prevent blood from flowing backward. If these valves fail to function properly, blood can pool in the veins, leading to their enlargement.
Anatomical abnormalities: Some individuals may have anatomical variations that predispose them to varicoceles.
Increased pressure in the abdomen: Conditions that increase pressure within the abdomen, such as heavy lifting, straining during bowel movements, or prolonged standing or sitting, can contribute to the development of varicoceles.
Symptoms:
Varicoceles may not always cause noticeable symptoms, but when symptoms do occur, they can include.
Visible or palpable enlargement: The most common symptom is the presence of a lump or mass in the scrotum. This may be more noticeable when standing and may disappear when lying down.
Pain or discomfort: Some individuals may experience a dull ache or pain in the scrotum, particularly after prolonged standing or physical activity.
Testicular atrophy: In severe cases or if left untreated, varicoceles can lead to testicular shrinkage or atrophy (size reduction).
Diagnosis:
Diagnosing varicoceles typically involves a combination of physical examination and imaging studies.
Physical examination: A healthcare provider may physically examine the scrotum while the patient is standing. They may ask the patient to perform a Valsalva maneuver (bearing down as if having a bowel movement) to increase intra-abdominal pressure, which can make the varicocele more prominent.
Ultrasound: Ultrasound imaging is often used to confirm the diagnosis of varicocele. This non-invasive imaging technique allows healthcare providers to visualize the veins within the scrotum and assess their size and condition.
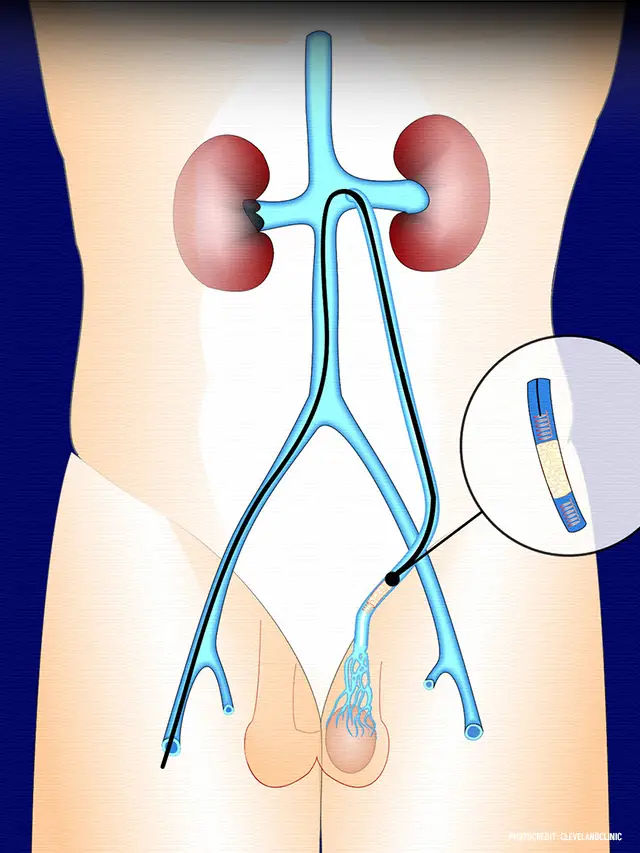
Venography: In some cases, venography may be performed to provide a more detailed assessment of the varicocele. This involves injecting a contrast dye into the veins of the scrotum and taking X-ray images to visualize blood flow and identify any abnormalities.
When Is Surgical Varicocele Treatment Necessary:
Surgical treatment for varicocele may be necessary under certain circumstances, including.
Criteria for Surgical Intervention:
Infertility: Varicoceles are a known cause of male infertility, affecting sperm quality and production. If a man experiences infertility and is diagnosed with a varicocele, surgical intervention may be recommended, especially if other potential causes of infertility have been ruled out.
Testicular Atrophy: Varicoceles can lead to testicular atrophy, where the affected testicle decreases in size due to reduced blood flow and oxygen supply. If testicular atrophy is observed or suspected, surgical correction of the varicocele may be necessary to preserve testicular function and fertility potential.
Persistent Pain or Discomfort: While not all varicoceles cause pain or discomfort, some individuals may experience chronic or intermittent pain in the scrotum. If conservative measures such as pain medication or wearing supportive underwear fail to alleviate symptoms, surgical treatment may be considered to relieve discomfort and improve quality of life.
Impact on Fertility and Testicular Health:
Varicoceles can adversely affect fertility and testicular health in several ways:
Sperm Quality: Varicoceles can lead to decreased sperm quality, including reduced sperm count, motility, and morphology (shape). Surgical correction of the varicocele may improve sperm parameters and fertility potential in affected individuals.
Testicular Function: The pooling of blood in the veins of the scrotum can increase the temperature of the testicles, which may impair spermatogenesis (sperm production). By restoring normal blood flow and reducing scrotal temperature, surgical treatment of varicocele may help preserve testicular function and prevent further damage.
Considerations for Pain or Discomfort:
For patients experiencing pain or discomfort associated with varicocele, surgical intervention may be considered if conservative measures are ineffective. However, it’s important to thoroughly evaluate the underlying cause of the pain and ensure that varicocele is indeed the primary contributor. Other conditions such as epididymitis, hydrocele, or inguinal hernia can also cause scrotal discomfort and should be ruled out.
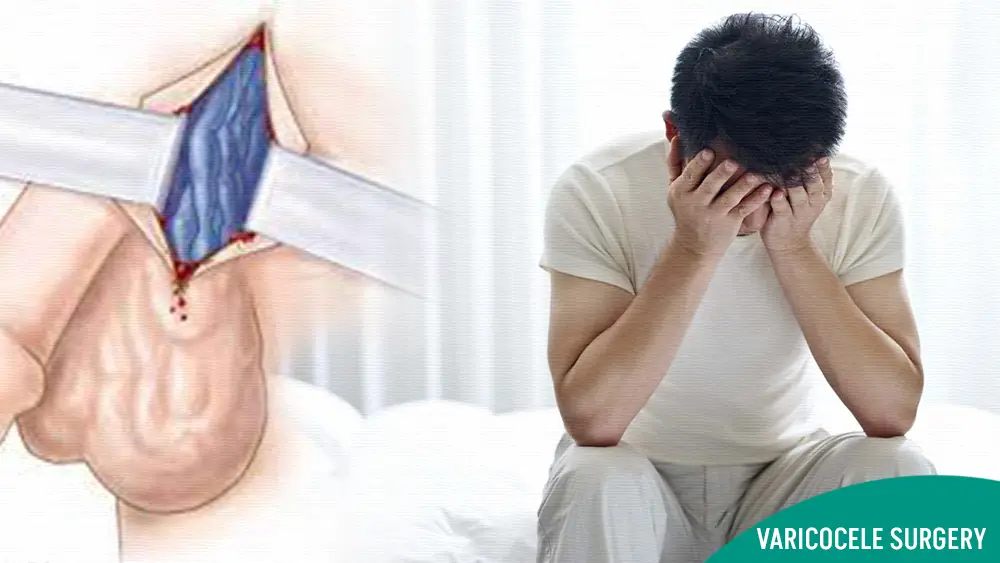
Types of Surgical Varicocele Treatments:
Open Surgical Varicocelectomy:
Open surgical varicocelectomy involves making an incision in the groin or lower abdomen to access and ligate (tie off) the dilated veins causing the varicocele. The surgeon may use loupe magnification or a surgical microscope to visualize and carefully dissect the veins, ensuring proper identification and ligation while preserving surrounding structures.
Pros and Cons: Pros: Open surgery provides direct access to the affected veins, allowing for precise ligation and potential correction of any associated anatomical abnormalities. It is often considered the gold standard treatment for varicoceles.
Cons: This approach requires a larger incision, resulting in longer operative times, increased postoperative pain, and a higher risk of complications such as hematoma (blood clot) or infection compared to minimally invasive techniques.
Recovery Timeline and Expected Outcomes: Recovery from open surgical varicocelectomy typically involves a few weeks of restricted activity and discomfort, with full recovery expected within 4 to 6 weeks. The success rate of open surgery in resolving varicoceles and improving fertility outcomes is generally high, with reported success rates ranging from 85% to 95%.
Laparoscopic Varicocelectomy:
Laparoscopic varicocelectomy involves making small incisions in the abdomen through which a laparoscope (a thin, flexible tube with a camera) and specialized surgical instruments are inserted. The surgeon uses the laparoscope to visualize and ligate the dilated veins, often with the assistance of intraoperative ultrasound for precise localization.
Advantages Compared to Open Surgical Varicocele Treatment: Less Invasive: Laparoscopic surgery requires smaller incisions, resulting in reduced postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times compared to open surgery.
Improved Cosmesis: Smaller incisions result in minimal scarring and better cosmetic outcomes.
Better Visualization: The laparoscope provides a magnified view of the surgical field, allowing for better visualization and precision during the procedure.
Recovery Process and Potential Complications from Surgical Varicocele Treatment: Recovery from laparoscopic varicocelectomy is generally quicker compared to open surgery, with most patients able to resume normal activities within a few days to a week. Potential complications may include bleeding, infection, or injury to surrounding structures, although these risks are generally lower than with open surgery.
Microsurgical Varicocelectomy:
Microsurgical varicocelectomy, also known as sublingual microsurgical varicocelectomy, is a highly specialized technique performed under magnification using an operating microscope. The surgeon makes a small incision in the groin and meticulously identifies and ligates the dilated veins, aiming to minimize trauma to surrounding tissues and preserve lymphatic drainage.
Success Rates and Post-operative Care: Microsurgical varicocelectomy is associated with high success rates, with reported improvement in sperm parameters and fertility outcomes in a significant percentage of patients. Post-operative care typically involves wearing scrotal support and avoiding strenuous activities for a few weeks to promote healing. Complications are rare but may include infection, hematoma, or recurrence of the varicocele.

Risks and Complications of Surgical Varicocele Treatment:
Common risks:
Bleeding: Bleeding during or after surgery is a potential complication, although it is usually minimal and can be controlled by the surgical team.
Infection: Surgical site infections can occur following varicocele surgery, leading to pain, swelling, redness, and possibly fever. Proper wound care and hygiene practices can help reduce the risk of infection.
Hematoma: The formation of a hematoma (blood clot) in the scrotum or surgical site is possible and may require drainage if it becomes large or painful.
Recurrence: While surgical varicocele treatment is generally effective, there is a small risk of varicocele recurrence, especially with open surgical techniques.
Testicular Atrophy: In rare cases, surgical intervention may inadvertently damage the testicular artery or lymphatic vessels, leading to testicular atrophy (shrinkage).
Hydrocele: Fluid accumulation around the testicle (hydrocele) can occur as a complication of surgery, although this is uncommon.
Strategies for Minimizing Complications:
Preoperative Evaluation: Thorough preoperative assessment, including medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies, can help identify any potential risk factors and optimize patient selection for surgery.
Surgical Technique: Surgeons with experience in varicocele surgery and specialized training in microsurgical or laparoscopic techniques can minimize the risk of complications by ensuring precise identification and ligation of the affected veins while preserving surrounding structures.
Prophylactic Antibiotics: The administration of prophylactic antibiotics before surgery can help reduce the risk of surgical site infections.
Postoperative Care: Proper wound care, pain management, and adherence to activity restrictions during recovery are essential for minimizing complications and promoting optimal healing.
Close Follow-Up: Regular follow-up appointments with the surgeon allow for early detection and management of any potential complications that may arise during the postoperative period.
When to Seek Medical Attention Post-Surgery:
Patients should promptly seek medical attention if they experience any of the following symptoms or complications after varicocele surgery.
– Persistent or worsening pain, swelling, redness, or warmth at the surgical site.
– Signs of infection, such as fever, chills, or purulent discharge from the incision site.
– Excessive bleeding or drainage from the incision site.
– Changes in testicular size, shape, or consistency.
– Difficulty urinating or signs of urinary tract infection.
Success Rates for Surgical Varicocele Treatment:
Factors Influencing Success:
Surgical Technique: The choice of surgical technique, such as open surgery, laparoscopic surgery, or microsurgery, can influence the success of varicocele treatment. Microsurgical techniques, in particular, have been associated with higher success rates and lower recurrence rates.
Surgeon Experience: The experience and skill of the surgeon performing the procedure play a significant role in the success of varicocele surgery. Surgeons with specialized training and expertise in varicocele treatment tend to achieve better outcomes.
Patient Selection: Proper patient selection based on factors such as age, fertility status, severity of varicocele, and presence of any underlying conditions affecting fertility can impact the success of surgical treatment.
Improvement in Fertility and Testicular Function:
Surgical Varicocele Treatment has been shown to improve sperm parameters, including sperm count, motility, and morphology, in a significant percentage of patients.
Improvement in fertility outcomes, such as increased pregnancy rates, has been reported following varicocele surgery, particularly in men with infertility or subfertility attributed to varicoceles.
Surgical correction of varicoceles may also help prevent further deterioration of testicular function and reduce the risk of testicular atrophy.
Long-Term Follow-Up and Recurrence Rates:
Long-term follow-up studies have demonstrated sustained improvements in sperm parameters and fertility outcomes following varicocele surgery, with pregnancy rates ranging from 30% to 60% in couples attempting to conceive naturally.
While surgical treatment can be effective in resolving varicoceles and improving fertility outcomes, there is a small risk of recurrence, particularly with open surgical techniques. Reported recurrence rates vary but are generally low, ranging from 1% to 15% depending on the surgical approach and patient factors.
Regular long-term follow-up with a healthcare provider is recommended to monitor fertility status, sperm parameters, and the need for additional interventions if varicocele recurrence or persistent infertility is suspected.
Patient Testimonials and Experiences regards Surgical Varicocele Treatment:
Testimonial 1: “After struggling with infertility for several years, my wife and I decided to explore potential causes. After undergoing testing, it was discovered that I had a varicocele. My urologist recommended surgical treatment as a possible solution. At first, I was hesitant about undergoing surgery, but after learning about the potential benefits, I decided to move forward.
The surgery went smoothly, and although there was some discomfort during the recovery period, it was manageable with pain medication. Within a few months, we noticed significant improvements in our fertility, and to our joy, my wife became pregnant shortly after. Today, we are proud parents, and I’m grateful for the decision to undergo varicocele surgery. It not only improved our chances of conceiving but also brought us closer as a couple.”
Testimonial 2: “I had been experiencing chronic pain and discomfort in my scrotum for years, and it was affecting my daily life. After consulting with a urologist, I was diagnosed with a varicocele and was told that surgical treatment could alleviate my symptoms. Initially, I was nervous about undergoing surgery, but the constant discomfort pushed me to proceed.
The surgery itself was straightforward, and the recovery was quicker than I expected. Within a few weeks, the pain and discomfort I had been experiencing for so long began to diminish. Now, several months post-surgery, I feel like a new person. The improvement in my quality of life has been remarkable, and I wish I had opted for surgery sooner. It’s amazing how such a simple procedure can have such a profound impact.”
FAQs about Surgical Varicocele Treatment:
A1: Surgical varicocele treatment involves procedures to ligate (tie off) the dilated veins within the scrotum that are causing the varicocele. These procedures aim to improve blood flow and alleviate symptoms associated with varicocele.
A2: Surgical treatment for varicocele may be necessary for individuals experiencing infertility, testicular atrophy, or persistent pain or discomfort that does not respond to conservative measures.
A3: Common surgical options include open surgical varicocelectomy, laparoscopic varicocelectomy, and microsurgical varicocelectomy. Each approach has its own advantages and considerations, depending on the patient’s needs and preferences.
A4: Risks and complications may include bleeding, infection, hematoma (blood clot), recurrence of varicocele, testicular atrophy, and hydrocele (fluid accumulation around the testicle). However, these complications are rare and can be minimized with proper surgical technique and postoperative care.
A5: Recovery from surgical varicocele treatment typically involves a few weeks of restricted activity and discomfort, with full recovery expected within 4 to 6 weeks. Patients may need to avoid strenuous activities and follow postoperative instructions provided by their healthcare provider. Regular follow-up appointments are also important to monitor recovery and address any concerns.
-Please remember, to always consult with healthcare professionals or Doctors for personalized advice related to medical conditions.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, surgical varicocele treatment stands as a viable option for individuals grappling with the challenges posed by varicoceles. Through this article, we have delved into the intricacies of varicocele, its diagnosis, and the circumstances necessitating surgical intervention. Understanding the causes and symptoms of varicoceles is pivotal in recognizing when surgical treatment becomes imperative, especially concerning factors such as infertility, testicular atrophy, or persistent discomfort.




