HEALTH NEWS
Optimizing Healthcare: Redesigning Gene Therapy with AI-Enhanced Protein
-
Rahul Priydarss
F
ocuses on optimizing proteins to mitigate immune responses, promising improved efficacy and reduced side effects in gene therapy.
Table of Contents
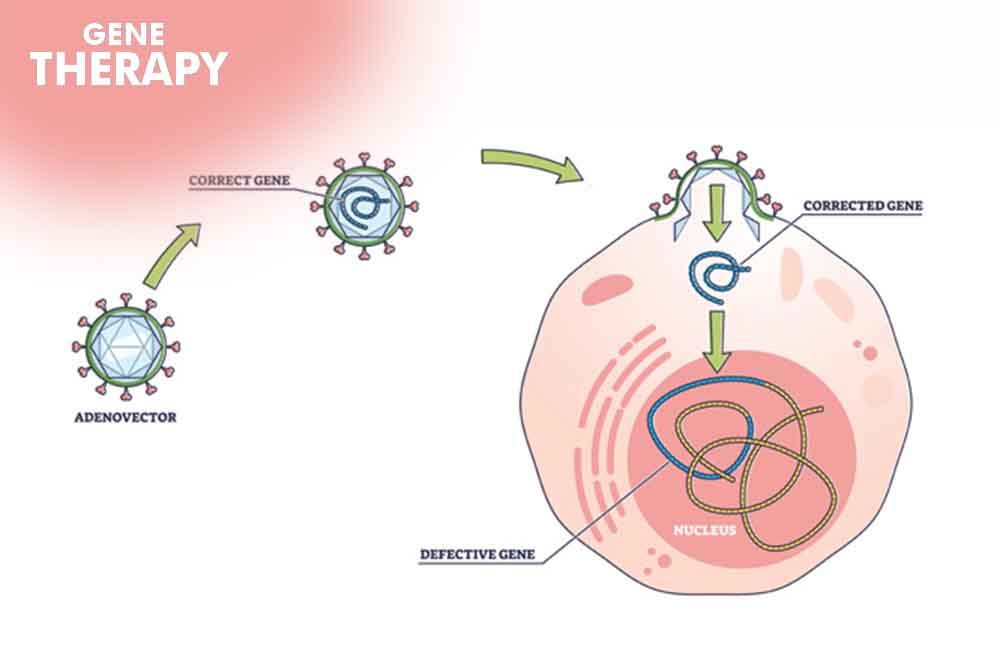
What Is Gene Therapy:
Researchers have harnessed the capabilities of artificial intelligence (AI) to revolutionize gene therapy by redesigning a crucial protein involved in the delivery process. This breakthrough, detailed in the journal Nature Machine Intelligence, focuses on optimizing proteins to mitigate immune responses, promising improved efficacy and reduced side effects in this therapy.
The Immune Challenge in This Therapy:
Assistant Professor Michael Garton from the University of Toronto acknowledges the immense promise of gene therapy but highlights the significant hurdle posed by the body’s pre-existing immune response to viral vectors. This challenge led the research team to zero in on hexons, fundamental proteins in adenovirus vectors, which hold tremendous potential for this therapy if not for the immune problem.
Targeting Hexons for Immune Resilience:
Immune responses triggered by specific antibodies obstruct the precise targeting of gene therapy vehicles, resulting in reduced efficacy and severe adverse effects. To overcome this, Garton’s lab employed AI to custom-design hexon variants that deviate from natural sequences, aiming to create structures unrecognizable by the immune system.
AI-Driven Protein Design: ProteinVAE Framework:
Traditional methods of protein design involve extensive trial and error, incurring high costs. The researchers introduced the AI framework, ProteinVAE, specifically tailored for designing long proteins like hexons. Unlike larger models, ProteinVAE efficiently learns from limited data, supporting fast training and inference on standard GPUs without demanding high computational resources.
ProteinVAE’s Generative Capability:
The AI model, validated through molecular simulation, demonstrates a remarkable ability to alter a significant percentage of the protein’s surface. This transformative feature potentially allows the redesigned proteins to evade immune responses, enhancing their effectiveness in gene therapy.
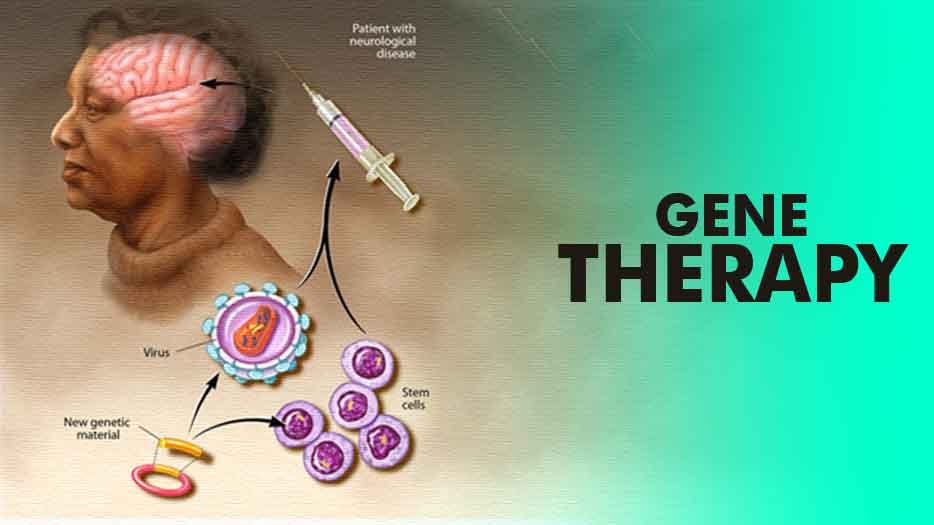
Beyond Gene Healing: Potential Applications in Medicine:
Lead author Suyue Lyu, a Ph.D. candidate, envisions broader applications for the AI model beyond gene therapy protein design. The researchers believe that ProteinVAE could be extended to support protein design in various disease cases, indicating the potential to design new biological entities with therapeutic value for novel medical treatments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
A1: AI plays a crucial role in redesigning proteins, specifically hexons, involved in gene healing. By custom-designing variants with AI, researchers aim to mitigate immune responses, improving the overall efficacy of gene healing.
A2: Hexons, fundamental proteins in adenovirus vectors, hold immense potential for gene therapy. Despite immune challenges, researchers believe hexons can be key to advancing gene therapy by using AI to create variants unrecognizable by the immune system.
A3: ProteinVAE, an AI framework, stands out for efficiently learning from limited data and designing long proteins like hexons. Its generative capability, demonstrated through molecular simulation, offers the potential to alter protein surfaces, evading immune responses in gene therapy.
A4: Yes, researchers believe the AI model, ProteinVAE, could have broader applications. Lead author Suyue Lyu envisions its use beyond gene therapy, suggesting the potential for designing new biological entities for various disease cases, paving the way for innovative medical treatments.

-Remember, Always consult with healthcare professionals or Doctors for personalised advice related to medical conditions.
Conclusion:
This pioneering research marks a significant stride in advancing gene healing through AI-driven protein design. By addressing the immune challenges associated with gene therapy, the researchers have opened doors to more effective and targeted treatments. The versatility of the ProteinVAE framework suggests its potential applicability in diverse medical scenarios, offering hope for the creation of innovative therapeutic solutions through generative AI. The intersection of AI and gene healing heralds a new era in medical research, promising transformative breakthroughs with far-reaching implications for the future of healthcare.
Previous Post