HEALTH BLOG
Unraveling Microvascular Brain Disease: Symptoms, Types, and Treatment Approaches
-
 Rahul Priydarss
Rahul Priydarss - February 14, 2024
Discover the complications of microvascular brain disease in our comprehensive guide. Highlight its symptoms, different types and effective treatment options. Gain insight into managing this condition for better neurological health.
What Is Microvascular Brain Disease:
– Microvascular brain disease, also known as small vessel disease (SVD) or small vessel ischemic disease, refers to a condition that causes damage to the small blood vessels in the brain. These small blood vessels, which are vital for supplying oxygen and essential nutrients and minerals to various areas of the brain, can become narrowed, blocked, or leaking due to a variety of factors, including high blood pressure, diabetes, aging, and other potential risk factors.
– This type of damage caused by microvascular brain disease can cause many neurological symptoms, such as cognitive impairment, memory loss and concentration problems in any work, frequent mood swings, problems with balance and coordination, and severe In cases, stroke. Subsequent MRI scans reveal white matter changes, lacunar infarcts, and microbleeds, which are typical features of this type of condition.
Table of Contents
Types Of Microvascular Brain Disease:
Here are some types of microvascular brain disease:
- Cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD)
- Cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA)
- Cerebral Autosomal Dominant Arteriopathy with Subcortical Infarcts and Leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL)
1- Cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD): It is a broad term used to describe a group of conditions that affect the small blood vessels in the brain. CSVD includes several subtypes, such as:
- White Matter Hyperintensities(WMH): Here there are areas of increased signal intensity in brain imaging, such as MRI, which indicate damage or changes in the white matter of the brain. WMH is a type of issue that is usually associated with aging and conditions like high BP and sugar.
- Lacunar infarcts: These are small and deep areas of damage to brain tissue caused by the blockage of small veins or arteries. This may result in symptoms such as weakness on one side of the body and other changes.
- Microbleeds: These are very small areas of bleeding in the brain, often seen as small black dots on MRI scans. Microbleeds are associated with conditions such as high blood pressure and cerebral amyloid angiopathy.
- Perivascular spaces: These are fluid-filled spaces around blood vessels in the brain. Perivascular spaces may widen with aging and conditions.
2- Cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA): This condition is characterized by the accumulation of amyloid protein in the walls of small blood vessels in the brain. They weaken blood vessel walls and increase the risk of bleeding and hemorrhagic stroke.
3- Cerebral Autosomal Dominant Arteriopathy with Subcortical Infarcts and Leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL): This is a very rare genetic disease caused by a mutation in the NOTCH3 gene, which causes thickening of the walls of small blood vessels in the brain. CADASIL can result in repeated strokes, cognitive decline, and a variety of other neurological symptoms.
4- Binswanger’s disease: Known as subcortical vascular dementia, Binswanger’s disease is a type of dementia that is caused by damage to small blood vessels in the deep white matter of the brain. They are associated with some symptoms such as progressive cognitive decline, mood changes, walking difficulties, and others.
5- Ischemic small vessel disease: It refers to conditions where small blood vessels in the brain become too narrowed or blocked leading to reduced blood flow and oxygen supply to certain areas of the brain. This ischemic small vessel disease can result in lacunar infarction, white matter changes, and other neurologic symptoms.
Symptoms Of Microvascular Brain Disease:
Some common symptoms associated with microvascular brain disease include:
1- Cognitive impairment: This may include difficulties with memory, concentration, attention, and executive functioning (planning, decision-making, etc.).
2- Motor impairment: Patients may experience difficulties with balance, coordination, and walking due to damage to the brain’s motor pathways.
3- Mood changes: Many individual people may experience mood changes, depression, anxiety, or emotional instability (rapid changes in emotions).
4- Changes in gait: Difficulty walking or changes in walking pattern, such as shuffling or dragging the legs.
5- Urinary symptoms: Bladder control problems may occur, including urinary urgency, frequency, or incontinence.
6- Headaches: Some individuals may experience headaches, which may vary in intensity and frequency.
7- Visual disturbances: Blurred vision, double vision, or visual field defects may occur due to damage to the brain’s visual pathways.
8- Fatigue: Chronic fatigue or exhaustion may be present, which is often exacerbated by the cognitive and physical challenges associated with the condition.

Causes and Affecting Factors:
Many factors may contribute to the development of microvascular brain disease, and some factors may vary from patient to patient. Some common causes and influencing factors include:
1- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): Major high blood pressure can damage small blood vessels of the brain, and then cause microvascular brain disease. However the constant pressure on the walls of blood vessels can cause them to narrow and less flexible, which can restrict blood flow to certain areas of the brain.
2- Diabetes: Diabetes or sugar is another risk factor for microvascular brain disease. If a patient or person is suffering from high blood sugar levels it can damage the blood vessels throughout the body including the brain. This type of damage can restrict blood flow and increase the risk of developing small vessel disease.
3- Smoking: Smoking is a very important risk factor for various vascular diseases, including this disease. The chemicals present in tobacco, gutkha, and cigarette smoking can damage blood vessels and cause inflammation, which can lead to small vessel disease in the brain.
4- Aging: As people age, the blood vessels in the brain become older, less flexible, and more likely to be damaged due to age. In addition, other age-related factors such as increased inflammation and oxidative stress may contribute to the prevalence of microvascular brain disease.
5- High Cholesterol: Increased levels of cholesterol in the blood can lead to plaque formation in the blood vessels, known as atherosclerosis. It can narrow blood vessels and reduce blood flow to the brain, increasing the risk of microvascular disease.
6- Obesity: Being gross or obese increases the risk of high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol, all of which are risk parts for microvascular brain disease. Also, fatness itself may contribute to inflammation and vascular dysfunction, further raising the risk.
7- Genetics: Some people may have a genetic susceptibility to microvascular brain disease. Clear genetic factors can influence the structure and function of blood vessels, predisposing them to damage and dysfunction.
Treatment:
Treatment of microvascular brain disease generally involves managing the underlying risk points and addressing the symptoms to prevent further damage and improve quality of life. Here are some common awards.
1- Blood Pressure Management: Because hypertension is a major risk factor for microvascular brain disease, it is important to control blood pressure through lifestyle modifications and medications.
2- Diabetes Management: Dense control of blood sugar levels is essential for diabetic patients to prevent further damage to the small blood vessels in the brain.
3- Cholesterol Management: Reducing cholesterol levels, especially LDL cholesterol, may help reduce the risk of further microvascular damage.
4- Smoking Cessation: Smoking damages blood vessels and causes microvascular disease. It is important to avoid or quit smoking to prevent the condition from progressing.
5- Antiplatelet Therapy: Certain medications, such as aspirin or clopidogrel, may be prescribed to prevent blood clots and reduce the risk of stroke in individuals with microvascular disease.
6- Anticoagulant Therapy: In some cases, certain anticoagulant medications may be necessary to prevent blood clots from forming in small blood vessels in the brain.
7- Symptomatic Treatment: Depending on the symptoms experienced, medications may be prescribed to manage issues such as cognitive impairment, depression, or headaches.
8- Lifestyle Modifications: Acquiring a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, a healthy weight, and managing stress, may help improve overall vascular health and slow the development of microvascular brain disease.
9- Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation: For many individuals experiencing mobility or balance problems due to microvascular brain disease, physical therapy, and rehabilitation programs may be favorable in improving function and mobility.
10- Regular Monitoring: Near monitoring by healthcare professionals is important to assess disease progression, adjust treatment as needed, and provide required support and guidance to patients and their families.
FAQs Microvascular Brain Disease:
A1: Microvascular brain disease, also known as small vessel disease (SVD), refers to a condition where the small blood vessels in the brain are damaged. This damage can lead to various neurological symptoms and is often associated with risk factors like high blood pressure, diabetes, and aging.
A2: Common symptoms include cognitive impairment, motor difficulties, mood changes, changes in gait, urinary symptoms, headaches, visual disturbances, and fatigue.
A3: Types include cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD), cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA), CADASIL, Binswanger’s disease, and ischemic small vessel disease.
A4: Contributing factors include hypertension, diabetes, smoking, aging, high cholesterol, obesity, and genetic predisposition.
A5: Treatment involves managing underlying risk factors such as blood pressure, diabetes, and cholesterol levels. Lifestyle modifications, medications, and therapies like physical therapy may also be recommended. Regular monitoring is essential to track disease progression.
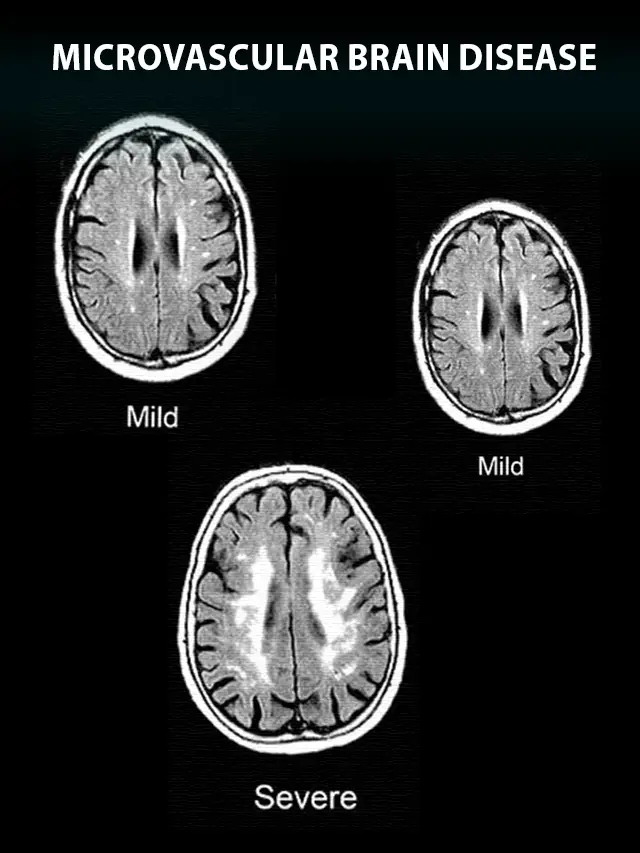
-Please remember, to always consult with healthcare professionals or Doctors for personalised advice related to medical conditions.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, microvascular brain disease, also known as small vessel disease (SVD), encompasses a variety of conditions that cause damage to the small blood vessels in the brain. This damage can lead to a variety of neurological symptoms, including cognitive impairment, mood changes, motor difficulties, and urinary problems.




