HEALTH BLOG
Potts Disease Symptoms and Causes Explained Everything You Need to Know
-
Rahul Priydarss
Discover the ins and outs of Potts disease with our comprehensive guide. Learn about the symptoms, treatment options, and practical tips for living well with spinal tuberculosis. Get expert information and advice to effectively manage Potts disease.
Introduction to Potts Disease:
Basics OF Potts Disease: Pott’s disease, also known as spinal tuberculosis, is a form of tuberculosis that primarily affects the spine. Named after the British surgeon Sir Percival Pott, who first described the condition in the 18th century, Pott’s disease is characterized by infection of the vertebrae by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
– Unlike pulmonary tuberculosis, which affects the lungs, Pott’s disease specifically targets the bones and tissues of the spine. Infection typically occurs when tuberculosis bacteria spread through the bloodstream and settle in the vertebrae, causing inflammation, destruction of bone tissue, and sometimes the formation of abscesses.

Table of Contents
Causes and Risk Factors of Potts Disease:
Pott’s disease, also known as spinal tuberculosis, is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This bacteria mainly affects the spine, causing inflammation, destruction of bone tissue, and other complications. Understanding the causes and risk factors for Potts disease is important to identify individuals who may be at greater risk of developing the condition.
Causes:
Pott’s disease is primarily caused by the same bacterium that causes tuberculosis, Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infection usually occurs when tuberculosis bacteria spread through the bloodstream and settle in the spinal cord. Once bacteria establish themselves in the bone tissue, they can grow and cause inflammation, leading to the symptoms of Pott’s disease.
Risk Factors:
Several factors can increase the risk of developing Pott disease.
- Exposure to tuberculosis: Individuals who have been exposed to tuberculosis through close contact with an infected person or by living in areas with high rates of tuberculosis have an increased risk of developing Potts disease.
- Weakened immune system: A weakened immune system, such as caused by conditions such as HIV/AIDS or certain medications (e.g., corticosteroids), can make individuals more susceptible to tuberculosis infection and may increase the chance of developing Potts disease.
- Poor nutrition: Malnutrition and poor dietary intake can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to tuberculosis infection and its complications, including Pott’s disease.
- Living conditions: Overcrowding and poorly ventilated living conditions can promote the spread of tuberculosis bacteria, increasing the risk of infection and the subsequent development of Potts disease.
- Patient Age: While Pott’s disease can affect individuals of all ages, it is more common in children and young adults, possibly due to their developing immune systems and increased likelihood of exposure to tuberculosis.
- Travel: Traveling to or living in areas with high rates of tuberculosis increases the risk of exposure to the bacteria, which increases the risk of developing Potts disease. Understanding these causes and risk factors may help healthcare providers identify individuals who may be at greater risk for developing Potts disease.
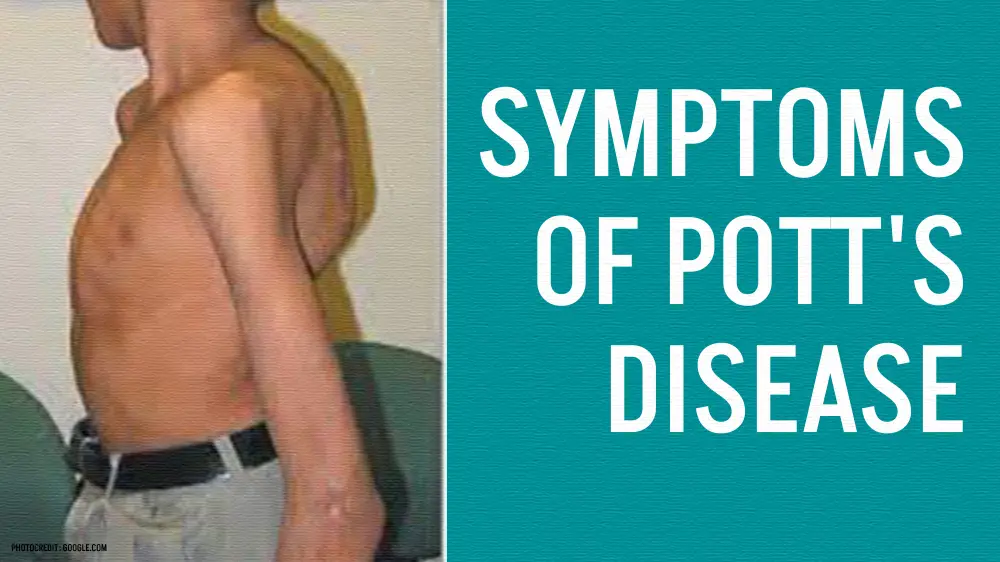
Symptoms of Potts Disease:
Pott’s disease, also known as spinal tuberculosis, manifests with a variety of symptoms that can affect a person’s spine and overall health. It is important to recognize these symptoms for early diagnosis and prompt treatment. Here are the common symptoms associated with Potts disease.
- Persistent back pain: One of the major symptoms of Pott’s disease is persistent back pain, which can get worse over time. The pain is often localized to the affected area of the spine and may increase with movement or physical activity.
- Stiffness and limited mobility: Patients with Pott disease often experience spinal stiffness and limited mobility. This stiffness can make it challenging to bend, turn, or perform everyday activities comfortably.
- Neurological symptoms: As the infection progresses, it can put pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots, resulting in neurological symptoms such as numbness, tingling or weakness in the limbs. In severe cases, patients may become paralyzed or have difficulty controlling bowel and bladder function.
- Spinal Malformation: Advanced Potts disease can cause spinal deformities, causing curvature or bending of the back. This can result in abnormalities in posture and affect a person’s physical appearance.
- Systemic Symptoms: In addition to specific spinal symptoms, individuals with Pott disease may also experience systemic symptoms such as fever, night sweats, fatigue, and unintentional weight loss. These symptoms indicate the body’s immune response to infection.
- Difficulty in breathing: In cases where Pott’s disease affects the thoracic spine (mid-back region), patients may experience difficulty breathing due to pressure on the lungs or surrounding structures. This symptom may worsen as the infection progresses.
How To Live With Potts Disease And Tips:
Living with Pott’s disease, also known as spinal tuberculosis, can present various challenges due to the impact it can have on daily life and overall well-being. However, with proper management and support, individuals affected by Pott disease can live fulfilling lives. Here are some tips for dealing with Pott’s disease and living a good life.
- Educate yourself: It is essential to understand Potts disease, its symptoms, treatment options, and possible complications. Take the time to educate yourself about the condition and don’t hesitate to ask your healthcare provider any questions you have.
- Follow your treatment plan: It is important to follow your prescribed treatment plan to manage Pott’s disease effectively. This may include taking antibiotics as directed, attending regular medical appointments, and following any additional recommendations from your health care team.
- Practice good posture: Maintaining good posture can help reduce back pain and prevent further stress on the spine. Be mindful of your posture when sitting, standing, and lifting objects, and consider using a supportive cushion or pillow if necessary.
- Stay active: Engaging in regular physical activity can help strengthen the muscles around the spine and improve flexibility. However, it is important to choose low-impact activities that are gentle on the spine, such as walking, swimming or yoga. Consult your healthcare provider before starting any new exercise program.
- Manage the pain: Chronic back pain is a common symptom of POT, but there are various strategies to manage the pain effectively. This may include over-the-counter pain relievers, hot or cold therapy, light stretching exercises, or techniques such as acupuncture or massage therapy. Work with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized pain management plan.
- Get help: Living with a chronic condition like bowel disease can be emotionally challenging. Don’t hesitate to reach out to friends, family members, or support groups for emotional support and encouragement. Talking to other people who are going through similar experiences can provide valuable insight and reassurance.
- Prioritize self-care: Taking care of your physical and mental well-being is essential when living with Potts disease. Make time for relaxation, hobbies, and activities that bring you joy. Practice stress reduction techniques like deep breathing, meditation or mindfulness to help manage anxiety and improve overall quality of life.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Eating a balanced diet, getting adequate amounts of sleep, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption can help support your overall health and immune system, which can help live with Potts disease. But is especially important.
- Stay positive: While living with Potts disease can present challenges, maintaining a positive attitude can make a significant difference in your overall well-being. Focus on the things you can control, celebrate your successes, and be patient with yourself as you move through your journey with the situation.
- Communicate with your healthcare team: Open and honest communication with your healthcare providers is essential to effectively managing Potts disease. Keep them informed about any changes in your symptoms or your concerns and work together to adjust your treatment plan as needed.
FAQs About Pott’s Disease:
A1: Pott’s disease, also known as spinal tuberculosis, is a form of tuberculosis that primarily affects the spine. It occurs when the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis infects the vertebrae, causing inflammation, bone destruction, and other complications.
A2: Common symptoms of Pott’s disease include persistent back pain, stiffness, neurological symptoms (such as numbness or weakness in the limbs), fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Specific symptoms may vary depending on the severity and location of the infection.
A3: Diagnosis of Pott’s disease usually involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, imaging tests (such as X-ray, CT scan, or MRI), and sometimes laboratory testing (such as blood tests or biopsy of the affected tissue). Is. Early diagnosis is important to prevent further damage to the spinal cord and improve treatment outcomes.
A4: Treatment of Pott’s disease usually involves a combination of antibiotics to eliminate the tuberculosis bacteria, along with supportive measures such as rest, pain management, and physical therapy. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to stabilize the spine or remove abscesses.
A5: With prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment, the prognosis of Pott disease is generally favorable. Many patients experience significant improvement in symptoms and quality of life with appropriate management. However, results may vary depending on individual factors such as the severity of the infection, the presence of complications, and overall health and immune status.
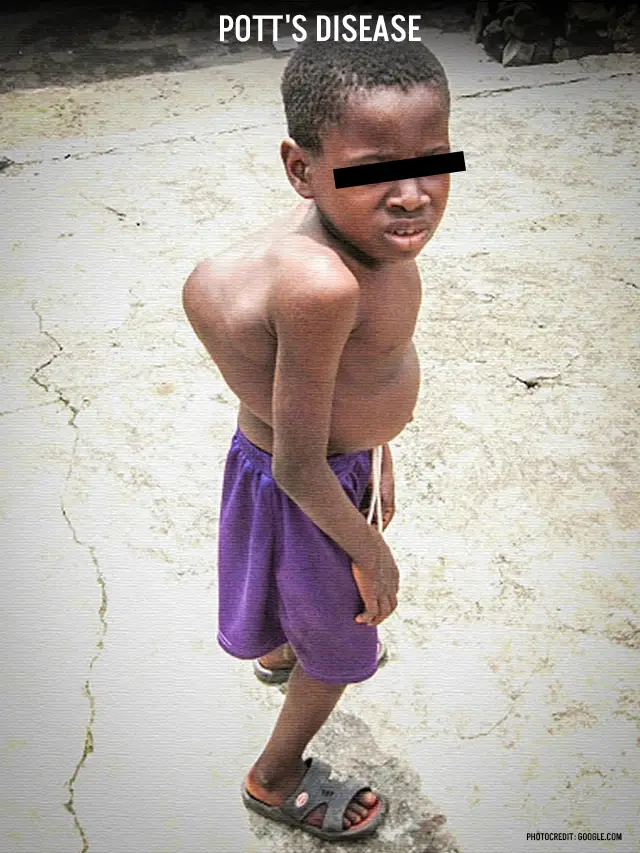
-Please remember, to always consult with healthcare professionals or Doctors for personalised advice related to medical conditions.
Conclusion:
Understanding Pott’s disease is of paramount importance for individuals affected by this condition. Named after British surgeon Sir Percival Pott, it primarily targets the spine, causing inflammation, bone destruction, and possible abscess formation. Unlike pulmonary tuberculosis, Potts disease specifically affects the bones and tissues of the spine, causing persistent back pain, stiffness, neurological problems, fever, and weight loss.